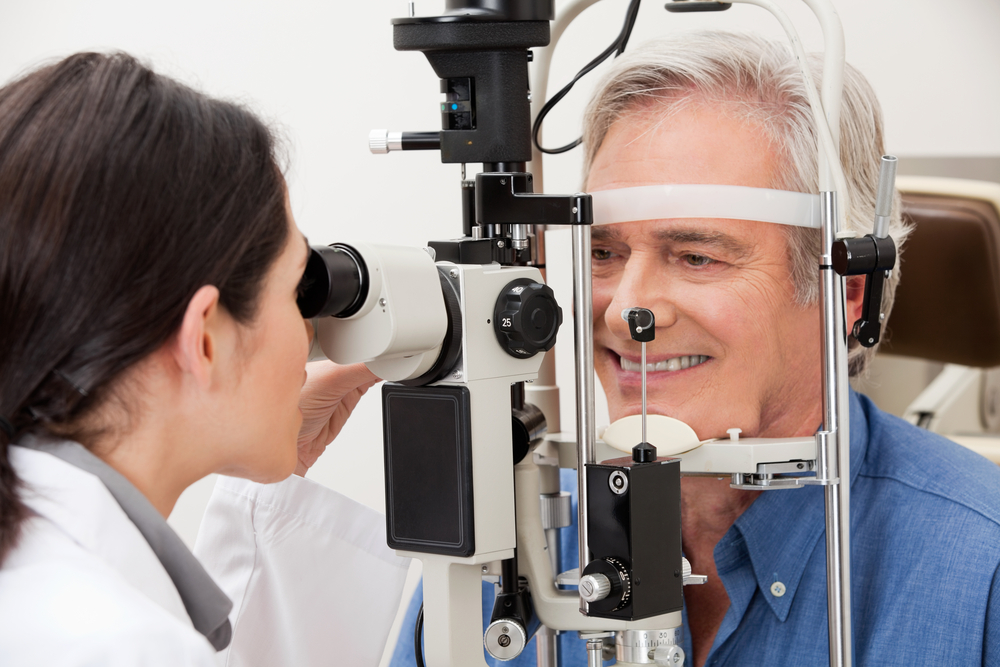
The belief that 80 percent of learning occurs through sight is enough reason to believe many vision-related learning problems. Such problems deter many people from accessing both basic and advanced education. The situation becomes worse among school-going children and younger people. This group’s most common visual problems include refractive errors like astigmatism, shortsightedness, and farsightedness. These may be easily corrected by using eyeglasses, but they come with more visual information processing problems in the brain. This article will highlight some common ways vision problems can affect learning.
The most obvious is difficulty seeing the board or reading a textbook or other materials. If your child is struggling to read information from their books or blackboard, this will affect the rate at which they can learn. For example, if a child has trouble reading the board clearly, they will not complete their work correctly or on time. Children who miss out on information displayed on the board for a lesson can fall behind their peers very quickly. The only leverage to these problems is performing eye exams on the patients to ascertain the visual problem’s nature and get the best remedy or treatment.
Also Read: Having Trouble Pairing Your Spotify With Other Devices, Here Is The Help
1. Eye strain and headaches
Children who have poor vision may experience eye strain and headaches due to the effort they must put in to focus on something. If your child complains of headaches after school, this could be a sign of poor vision.
2. Lack of Confidence
Whenever a child or any learner feels they are not sharp because of the inability to focus or concentrate on what is written may make them not try at all. Such a category of learners will feel so ‘dumb’ that they lose interest in school or homework. For instance, the fear that they will give wrong answers reduces their participation in class discussions with or without their instructors. A child with more confidence in their academic ability is better placed to succeed at school. But the ones with no faith in themselves will have lower morale. Fortunately, teachers with an early childhood education training can enhance their confidence. This training helps learners to develop the knowledge, skills, and confidence necessary to provide high-quality care and support.
3. Difficulty concentrating
Concentration depends on the ability to focus. Otherwise, if one cannot read the black or whiteboard or any screen can impede class concentration. Perhaps the problem is worse; it even prevents their ability to read books.
Whatever the problem is, it will affect the everyday learning condition that depends significantly on visual performance. If you fail to read the information presented, your Learning will be substantially impaired. Concentration gives a better chance of success in classwork that largely depends on instructional methods—the more the focus and concentration, the better the retention capability.
4. Poor Hand-Eye Coordination
Learning is a good thing, just as good as recess. Every average human needs a break between the regular classwork to recharge and freshen the mind. This is the essence of a well-rounded education that supports a child’s mental health.
Unfortunately, learners with vision problems will avoid all kinds of co-curricular activities because they lack hand-eye coordination. Meaning they cannot use some of their body parts properly as they have a problem with timing and depth perception. Some may not participate in sports, hence the fatigue caused by learning without a mental break.
There are other not-so-obvious ways that children with poor vision struggle in the classroom:
5. Fatigue
Students with uncorrected vision problems are more likely to suffer from eye strain, headaches, and fatigue. And these symptoms can lead to behavioral issues and lower academic performance.
6. Behavioral issues
Students with uncorrected vision problems may act out and have difficulty paying attention. Poor eyesight can cause children to have trouble focusing on their work. When they cannot see what’s happening around them, they may misbehave when they’re bored or frustrated.
7. Social isolation
Children who cannot see well often become socially isolated, as they cannot participate in group activities. This can lead to low self-esteem and depression.
8. Difficulty completing
Children who do not see well may not compete athletically because of decreased coordination and balance. Peers may also ridicule them for poor athletic performance, leading to social isolation.
Falling behind in school because of a vision-related learning impairment can hinder a child’s development and impair their ability to build fundamental skills. Make sure your child has the eye skills they need to excel in school by scheduling a full vision check to help them learn favorably.