Every matter involved in the world is made up of elements. Matter can be either solid, liquid or gas. The matter may be formed by the same elements or a combination of elements. It is said that matter originated from elements after cooling the universe by combining the protons, neutrons and electrons.
As elements play a major role in our daily lives in every aspect, it is a must to know about them and apply them in necessary areas. Together 118 elements are known to us to date.
Now let us understand what are the 118 elements of the periodic table in detail.
Also Read : The star of which sitcom shares his last name with a common type of wrench?
What is an element?
Any element can be defined as a pure chemical substance made up of only one atom, and its nuclei consist of the same numbers of protons as that of electrons. An element cannot be broken down into further simpler forms by chemical reaction.
Example: Oxygen, copper, gold, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
What do you mean by Element symbols/Chemical formulas?
Element symbols are abbreviations consisting of one or two letters from the Latin alphabet of the chemical element name and are written capitalising the first letter. It is represented by the symbol “X”. Certain details can be added as superscripts or subscripts to their element symbols like “A” (atomic number) and “Z” (mass number).
Atomic number (Proton number):
- It is the total number of protons in the nucleus of every atom for any element.
- It is represented by symbol Z
Mass number/ atomic mass number/nucleon number:
- It refers to the total number of protons and neutrons (nucleons) in an atomic nucleus.
- It is represented by symbol A
Before knowing about Elements in detail, let us make ourselves clear with key terms:
- Atoms are the building blocks of any substance in a solid, liquid or plasma state.
- Each atom is composed of small particles known as electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particle
- Protons are positively charged subatomic particles and a strong nuclear force binds them in the nucleus of an atom
- Neutrons are neutral subatomic particles with no charge, and a strong nuclear force binds them in the nucleus of an atom
- The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons
- Electrons are seen orbiting around the nucleus in ‘shells.’
- Shells are a set of electron orbitals having the same principal quantum number.
- Electronic configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals (s, p, d, f)
- Each orbital can only hold 2 electrons max and will be filled in the order s, p, d, and f
What are isotopes?
When atoms of the same element consist of different numbers of neutrons, they are called isotopes.
Example: 12C, 13C and 14C.
What are Allotropes?
The bonding of atoms in chemically pure elements in different ways gives different chemical structures known as allotropes.
Example: Carbon in diamond and graphite has different structural arrangements.
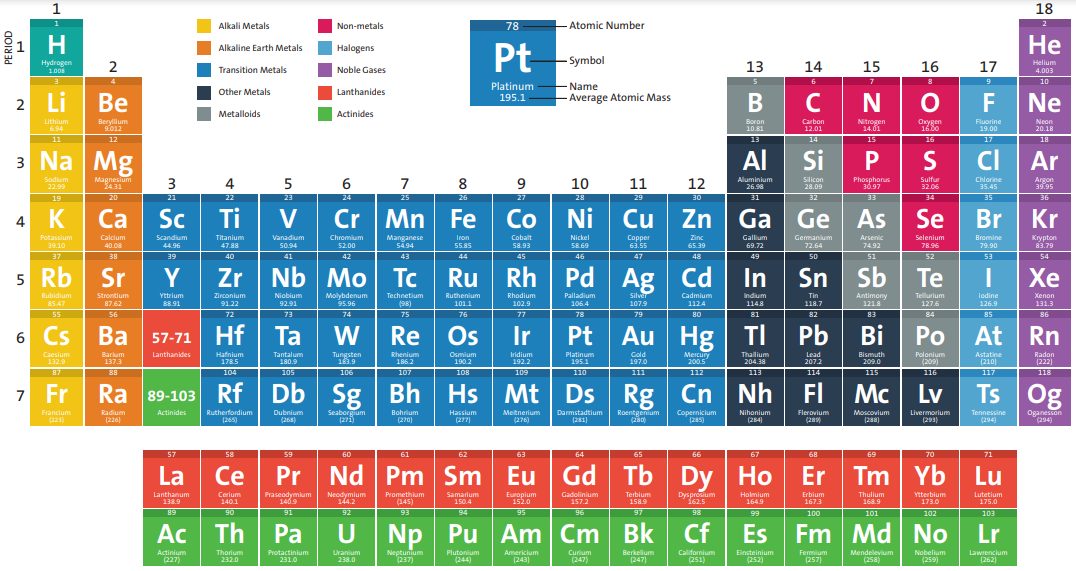
Modern Periodic table:
- Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) designed a tabular form for arranging elements.
- Modern periodic law states that “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
What is the periodic table composed of?
- It consists of 18 vertical columns called Groups and 7 series of rows called Periods.
- Periods fall into three categories, namely Short (1st, 2nd, 3rd), Long (4th, 5th, 6th) and Incomplete (7th) based on the number of elements they contain
- All group elements have the same number of outer electrons, sharing similar chemical and physical properties.
- Few groups are divided as A and B subgroups to make it more specific.
List of elements with their specific symbol and atomic number
| Element Name | Symbol of the Element | Atomic Number |
| Hydrogen | H | 1 |
| Helium | He | 2 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 |
| Boron | B | 5 |
| Carbon | C | 6 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 |
| Fluorine | F | 9 |
| Neon | Ne | 10 |
| Sodium | Na | 11 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 |
| Aluminium | Al | 13 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 |
| Phosphorus | P | 15 |
| Sulfur | S | 16 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 |
| Potassium | K | 19 |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 |
| Scandium | Sc | 21 |
| Titanium | Ti | 22 |
| Vanadium | V | 23 |
| Chromium | Cr | 24 |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 |
| Iron | Fe | 26 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 |
| Nickel | Ni | 28 |
| Copper | Cu | 29 |
| Zinc | Zn | 30 |
| Gallium | Ga | 31 |
| Germanium | Ge | 32 |
| Arsenic | As | 33 |
| Selenium | Se | 34 |
| Bromine | Br | 35 |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 |
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 |
| Strontium | Sr | 38 |
| Yttrium | Y | 39 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 |
| Niobium | Nb | 41 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 42 |
| Technetium | Tc | 43 |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 44 |
| Rhodium | Rh | 45 |
| Palladium | Pd | 46 |
| Silver | Ag | 47 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 48 |
| Indium | In | 49 |
| Tin | Sn | 50 |
| Antimony | Sb | 51 |
| Tellurium | Te | 52 |
| Iodine | I | 53 |
| Xenon | Xe | 54 |
| Cesium | Cs | 55 |
| Barium | Ba | 56 |
| Lanthanum | La | 57 |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 59 |
| Neodymium | Nd | 60 |
| Promethium | Pm | 61 |
| Samarium | Sm | 62 |
| Europium | Eu | 63 |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 |
| Erbium | Er | 68 |
| Thulium | Tm | 69 |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 |
| Tantalum | Ta | 73 |
| Tungsten | W | 74 |
| Rhenium | Re | 75 |
| Osmium | Os | 76 |
| Iridium | Ir | 77 |
| Platinum | Pt | 78 |
| Gold | Au | 79 |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 |
| Thallium | Tl | 81 |
| Lead | Pb | 82 |
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 |
| Polonium | Po | 84 |
| Astatine | At | 85 |
| Radon | Rn | 86 |
| Francium | Fr | 87 |
| Radium | Ra | 88 |
| Actinium | Ac | 89 |
| Thorium | Th | 90 |
| Protactinium | Pa | 91 |
| Uranium | U | 92 |
| Neptunium | Np | 93 |
| Plutonium | Pu | 94 |
| Americium | Am | 95 |
| Curium | Cm | 96 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 |
| Californium | Cf | 98 |
| Einsteinium | Es | 99 |
| Fermium | Fm | 100 |
| Mendelevium | Md | 101 |
| Nobelium | No | 102 |
| Lawrencium | Lr | 103 |
| Rutherfordium | Rf | 104 |
| Dubnium | Db | 105 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 106 |
| Bohrium | Bh | 107 |
| Hassium | Hs | 108 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 109 |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 |
| Roentgenium | Rg | 111 |
| Copernicium | Cn | 112 |
| Nihonium | Nh | 113 |
| Flerovium | Fl | 114 |
| Moscovium | Mc | 115 |
| Livermorium | Lv | 116 |
| Tennessine | Ts | 117 |
| Oganesson | Og | 118 |
Properties of Elements used for characterisation
- Metals (That conducts electricity), Non-metals (that does not conduct electricity) and metalloids (that have intermediate conductivity)
- The periodic table is classified as halogens, post-transition metals, metalloids, reactive nonmetals, noble gases, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides.
- States of matter at STP
- Elements can exist in different states of matter, i.e. as solids, liquids or gases at STP.
- Melting and boiling points of elements at one atmospheric pressure differ for each element and can be a factor in distinguishing.
- Densities: It is measured at standard temperature and pressure and used for characterising elements
- Crystal structures: Crystal structures of elements in the solid-state may be of eight different kinds, namely cubic, face-centred cubic, body-centred cubic, hexagonal, monoclinic, orthorhombic, tetragonal and rhombohedral.
- Basis of the occurrence on Earth: Some elements naturally occur, and few are man-made.
Conclusion
So now we are aware of all the 118 elements and their symbols and atomic numbers. These elements cannot be broken down into any other simpler form. Each element has a unique atomic number and on this basis are arranged in the periodic table in their increasing order. Vertical columns in the periodic table include elements with similar properties. Hydrogen is the lightest element known to date.